The packed cell volume (PCV) test is used to determine the proportion of blood constituted by red blood cells.
This test helps the physician know if your red blood cell volume is too high or too low.
It is also called the hematocrit test.
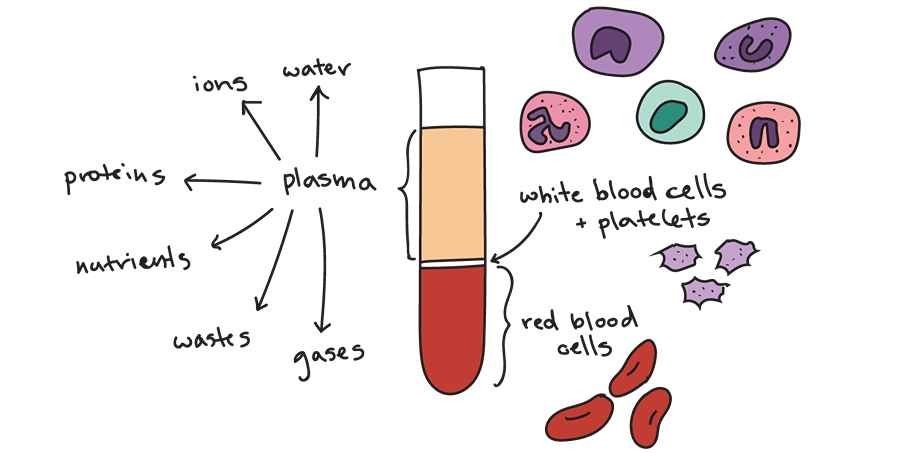
Blood is a collection of red and white blood cells suspended with platelets in a fluid called plasma.
These cells exist together in different volumes, which is key to the individual functions they perform in the body.
An increase or decrease in the red blood cell count can affect your health.
Since they carry oxygen from your lungs to other parts of your body, the red blood cells need to be at an appropriate level for them to meet the oxygen demand of your body.
The PCV test shows the proportion of red blood cells available to facilitate this supply.
Why do I need to do a PCV test?
Your physician may request a PCV test as part of a full blood count, or to:
- Evaluate the symptoms of anemia or polycythemia.
- Monitor the impact of pregnancy, dehydration, malnutrition, and burns on your red blood cell volume
- Determine the severity of blood loss or destruction, caused either by injury or infection
- Evaluate your response to treatment to control anemia or polycythemia
- Assess your blood level after a blood transfusion or surgery
What should I do before a PCV test?
You don’t need to do anything special before a PCV test.
It is a simple procedure that can be done at a moment’s notice.
Depending on your arrangement with your physician, your blood may be collected and sent to the laboratory, or you may have to:
- Visit a laboratory
- Register your name, age, gender, and contact details
- Submit yourself for blood collection
To collect your blood, a laboratory technician will tie a tourniquet around your arm, clean your skin with an antiseptic, and insert a syringe into your vein to draw blood.
This will cause a slight pain, but you’ll be fine in a few minutes.
In young patients, blood can be collected from the capillaries of the fingertips.
In the case of children and newborns, the heel may be used.
How is the test done?
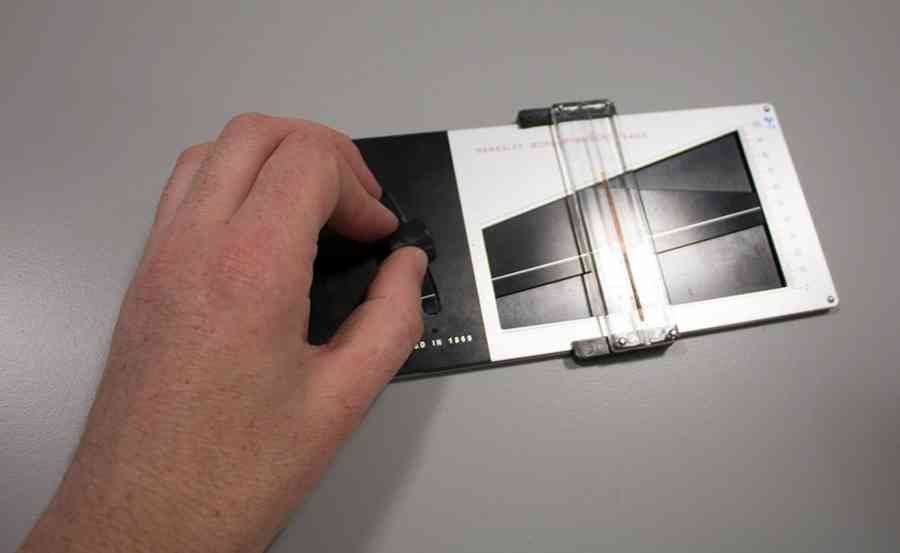

The PCV is a technical procedure that requires the service of skilled medical laboratory personnel.
Upon reception at the laboratory, a technician will:
- Transfer your blood into a tiny, heparinized capillary tube filled to about three-quarters of its length
- Seal the tube at one end with a sealant material. This is to prevent the blood from spilling during centrifugation
- Place the tube in one of the capillary slots on the rotor of a micro-hematocrit centrifuge. A blood sample with a known PCV value may be inserted into another slot as a control.
- Centrifuge the tubes for 5 minutes
- Read the result with a micro-hematocrit reader or calculate the value from the ratio of the height of the red blood column to the total column of blood in the capillary tube.
What should I do after a PCV test?
The test is a short one that can be conducted in under an hour.
Keep calm and wait for your test result.
Possible outcomes or results
The hematocrit value of the body typically ranges between 38.8 – 45.0%*.
However, this value varies with age, gender, and geography.
The normal range for adult males and females is given as:
- Male: 43.5 to 45.0%
- Female: 38.8 to 40.5%
A separate range is used for children and those with special conditions, like pregnancy.
Laboratories often have reference values for interpreting PCV test results.
Such values are provided either by the local health agencies or adopted from standard reference materials.
Regardless of the source of the reference values, a PCV test can produce three possible types of results:
- Normal: PCV value within the normal range
- Low: PCV value below the normal range
- High: PCV value above the normal range.
What does a PCV test result mean?
A PCV test result within the normal range shows that you are okay; your red blood cells are in the right quantity required for oxygen transport.
Your test will show a high PCV value if your red blood cell volume exceeds this quantity, while a low PCV value means that your red blood cells fall below the normal range.
In some cases, a high or low PCV value could be normal.
Normal variations in PCV value may be found in:
- Those living at a high altitude
- Pregnant women
- Blood transfusion recipients
Your test result could also demonstrate a disease.
If your PCV is too high, it may indicate:
- Dehydration
- Polycythemia vera
- Lung disease
- Congenital heart disease
- Kidney disease
A low PCV may be a result of:
- Bleeding
- Anemia
- Nutritional deficiency of vitamins and minerals
- Bone marrow disease
- Kidney failure
Conclusion
A PCV test gives insight into one of the chief characteristics of the blood: the capacity to transport oxygen.
A low proportion of red blood cells depletes this capacity.
On the other hand, a high red blood cell volume makes oxygen transport sluggish, thereby delaying oxygen supply to organs and tissues.
Whatever the result, a PCV test gives a clear picture of your blood’s oxygen transport capacity and, by extension, your health.
Bello Hussein
Bello Hussein is a medical student, content writer and journalist that writes medical and health-related contents for web and print.