1. Electronic Health Records (EHR)

An electronic health record (EHR) is a type of hospital management system designed for the record-keeping of patients’ health information, including details of demographics, symptoms, and signs, immunization history, examination findings, vital signs, diagnosis, test results, medications, treatment history, previous surgeries, allergies, charts, radiographs, etc., in digital form.
These health information systems are of immense use in health data management in the world today; they eliminate all the hassles associated with paper health record-keeping while introducing easy and fast ways to derive insight from health data.
Importantly, electronic health records allow for easy sharing of patients’ health information among authorized concerned parties for prompt patient care, including managing physicians, specialists, laboratories, etc.
This is especially useful when switching between health providers and health information has to be transferred to the new provider.
Understandably, these systems are designed with built-in security features to safeguard the process of handling patient data.
From collection to storage and, when needed, retrieval and transfer, there are measures to forestall and prevent compromise of the data and/or unauthorized access.
2. Electrical Medical Record (EMR)

An electronic medical record is a health information system designed to keep details of patients’ health information in digital form, it is the digital equivalent of paper patient records.
Electronic medical records (EMR) and Electronic health records (EHR) are two terminologies often used interchangeably or confused together however, they are not the same.
While both are applications of health information technology and are used in processing the health information of patients, they are distinct as EHR is more encompassing and broader than EMR.
The main advantage EHR has over EMR is that it is largely interoperable; it allows for easy, effective, and secure health data sharing, between different health facilities, health professionals, and really, any authorized organization.
The EMR on the other hand replaces the paper version of patients’ medical history and cannot be easily transferred from one health facility system to another as it is mainly used to document patient health information.
By being interoperable and more encompassing, EHR allows for active interactions between physicians and patients, real-time data sharing, and analysis of health data.
It aids decision-making in health facilities as the health data it processes can be used to derive insights into patient care.
EHR designs have enabled data sharing capacity across the globe as they are often employed by large health organizations to handle patient data.
On the contrary, EMRs are basic health information systems created as a digital equivalent of old-fashioned paper records, used by smaller facilities to process the health data of their patients, and are mainly capable of data storage and retrieval for the said individual facilities.
To transfer data from these EMRs, one might have to print the information on hardcopy paper.
3. Personal Health Records

A personal health record (PHR) is a health information system or application where patients can manage their health data, update their health information, share the data with trusted parties and they can as well authorize health providers to gain access to the data.
These records are usually of basic simple design, not as complex nor robust as electronic health/medical records, and give patients control of their health data.
PHRs have proven to be very secure private data management systems and can be designed as a standalone data system, or be linked with a robust electronic health record, or multiple record systems, for better data management.
The health data they process are usually patient-generated and the details vary from individual to individual, based on their health needs.
Common health records in health facilities are maintained and only accessible by healthcare providers and physicians, personal health records on the other hand are managed by the patient, the owner of the health data.
PHRs are usually available on mobile devices – smartphones, tablets, etc and can contain details of vital signs, diagnosis, allergies, blood glucose values, blood pressure measurements, hematology profile including blood group and genotype, chronic diseases, and prescription medications, etc
4. Patient portals
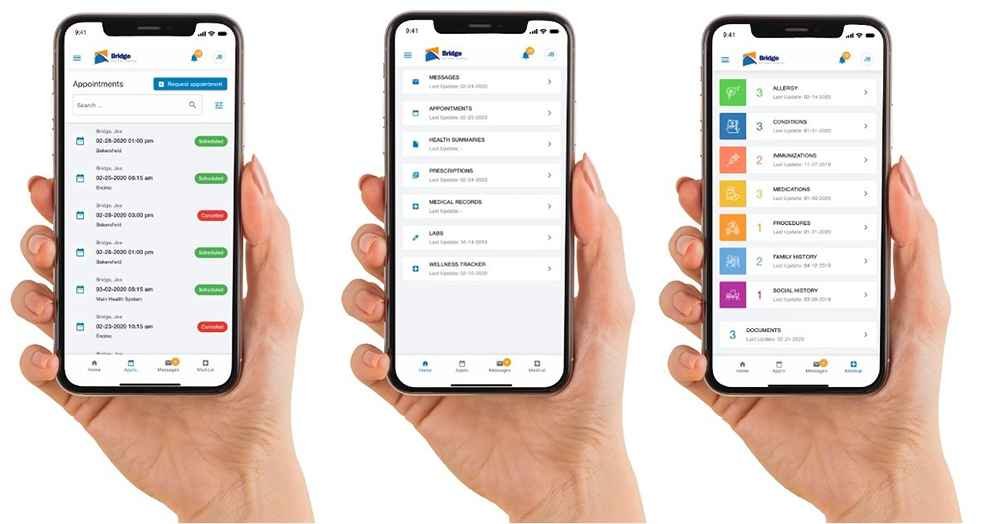
Patient portals are secure and save online accesses patients have to their health information and also their healthcare providers’ health information systems to view and/or update their data remotely and carry out activities like booking an appointment, managing health insurance, paying their health bills, etc
They are the mobile gateways for patients to access their health data stored away on the electronic health records platform of their healthcare provider.
These portals may include telemedicine features for patients to communicate with their managing physicians remotely.
More and more people now opt for health facilities with patient portal systems for appointment management – booking, updating, or cancellation.
This helps forestall the problem of patients not showing up for their booked appointments with their physicians, as these patients can easily log in to their account/portal and update their availability date if need be.
This introduces flexibility on the patients’ side, providing a better patient experience and increased engagement in their care, especially for patients with chronic medical conditions requiring routine monitoring.
5. Clinical decision support system (CDSS)
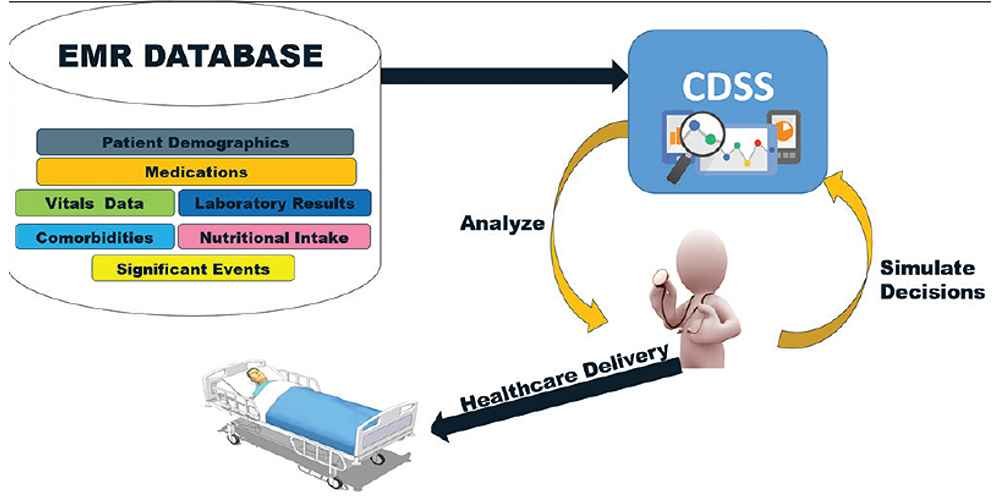
The clinical decision support system is a health information system developed to assist physicians and health professionals in patient care.
For a long time until now, decision-making in patient care has been based on health professionals’ training, clinical acumen, and sometimes discretion.
This approach to care has worked quite fine for decades howbeit, although subject to human errors.
This is where CDSSs come into play, they enable integrated workflow for patient care and help physicians map out a treatment plan for patients.
These health systems are designed to review the details of patient data, analyze them based on health data standards following medical principles, and thereafter make care recommendations.
In that they work on patient data, CDSSs are usually designed together with electronic health record (EHR) systems.
CDSS can combine patient symptoms towards making an accurate diagnosis, identify interactions among prescribed drugs, flag contraindications in investigations and radiographs like requesting an MRI in a patient with a metallic pacemaker, warn against wrong drug dosage, etc
Worthy of note, these systems only have assistive roles for which they offer recommendations after scanning through patient data, they are not given autonomy in designing management plans for patient care.
The suggestions are combined with the expertise and knowledge of the health professional to arrive at the needed decision for patient care.
Obisesan Damola
Damola is a medical doctor who has worked in the Nigerian healthcare industry for a little over 3 years in a number of primary, secondary, and tertiary hospitals. He is interested in and writes about how technology is helping to shape the healthcare industry. He graduated from the College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, the foremost medical training institution in Nigeria.



