Health Information Technology (HIT)

health information technology is a term that covers all types of electronic systems and devices used by healthcare professionals to support their work of managing patients, including those involved in patient consultations, and the processing, storage, sharing, and analysis of health information.
Wide adoption of health information technology aids in the delivery of quality healthcare, prevention of medical errors, reduction of healthcare costs, increases in administrative efficiencies, decreases in paperwork, expansion of access to affordable health care, improved efficiency of care, and ensures the safety of health professionals.
Health information technology (health IT) involves the processing, storage, and exchange of health information in an electronic environment – U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
The adoption of health information technology has experienced a rapid increase in recent times, this is due to several factors.
The healthcare industry constantly produces large sets of data, these patient and user data are stored in health information systems from where they are analyzed and insights are drawn from them to improve health outcomes.
These data are also available electronically hence, multiple healthcare providers and professionals who are authorized to access them can do so, allowing for multiple access to central health data by multiple health facilities/professionals.
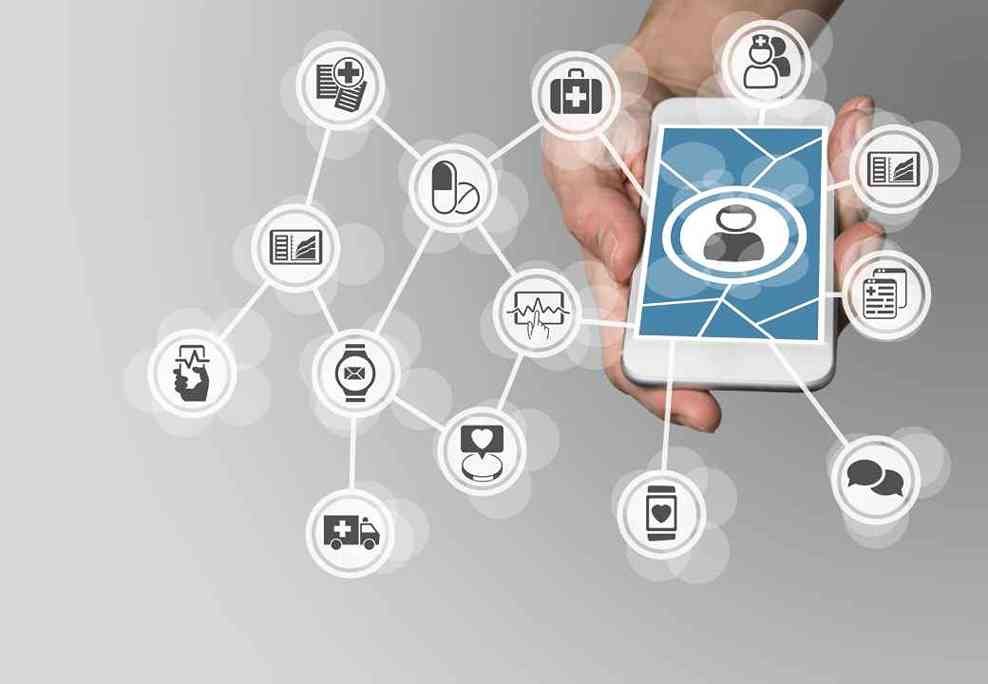

Also, patients are beginning to see the benefits of taking an active role in their health and personal information, health information technologies make available consumer solutions for personal data management that allow patients to take control and ownership of their data and long-term health outcomes.
The exchange of health data introduces decreases in data transfer costs as the use of digital networks to exchange healthcare data allows for efficiencies and cost savings.
Comparing HIT with similar disciplines
1. Health Information Technology vs Health Information Systems
A health information system (HIS) refers to a system in healthcare designed to manage, store, share, and analyze patient and user data collected in any healthcare facility, including systems that collect store, manage and transmit patients’ data, healthcare billing systems, operational management, policy decision systems, etc.
Health information technologies are the tools used to design and develop these health information systems.
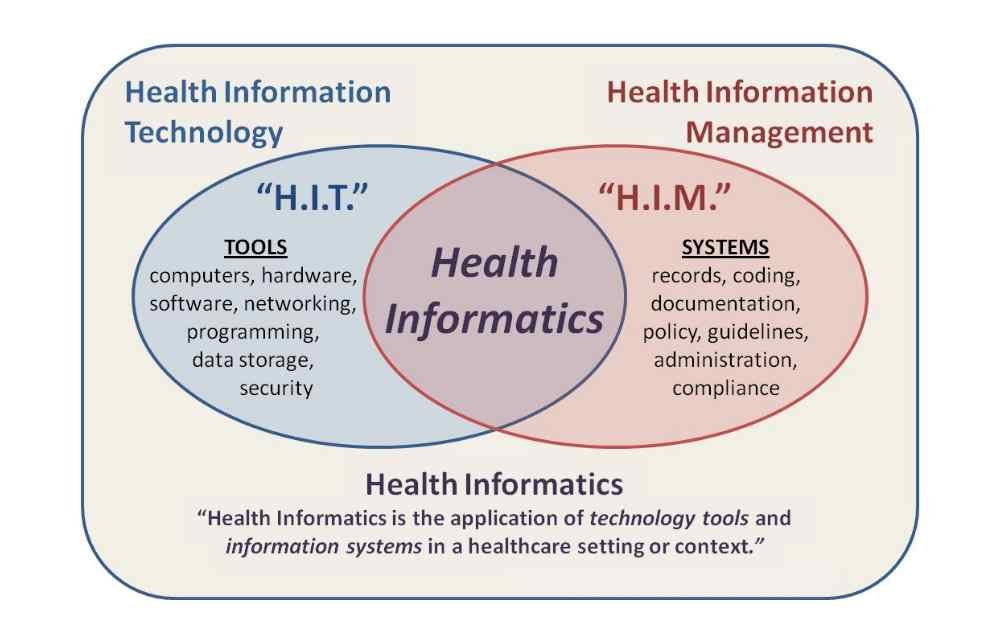
2. Health Information Technology vs Health informatics
Main post: Health Informatics
As much as there is an overlap between health information technology and health informatics, they are surely not the same.
HIT is the use of electronic technology tools by medical professionals and other healthcare organizations to gather, store, analyze, retrieve, and share patient data, a big part of which is EHRs.
Health informatics, however, applies insights from the analysis of patient data to improve health outcomes at an individual or population level.
Health information technology is made up of computer systems and their associated programs, while health informatics uses the said programs to achieve better patient outcomes and to understand trends and perceptions in the field of healthcare.
Health informatics professionals bridge the gap between HIT professionals and the end-users of their technology – Physicians, Nurses, Patients, etc.
Information technology (IT)
What you are doing right now, reading this blog post, involves information technology!
I came up with a website to write about health technology, this is the post on health information technology and I believe you are reading this right now because you are interested in knowing more about information technology in healthcare.
The term Information technology was coined by Harvard Business Review (HBR), to distinguish between general-purpose computing machines that could be programmed for different tasks and purpose-built machines that are specifically designed to perform a limited scope of functions.
While I can say reading this post involves information technology. some have argued the term only applies to commercial or business operations, not personal or entertainment purposes.
Information technology is the use of computers, storage, networking, and other physical devices, infrastructure, and processes to create, process, store, secure, and exchange all forms of electronic data – Tech Target
To put this in context, information technology has to do with the technologies involved in the connection and maintenance of all of a healthcare organization’s applications, data servers and storage, service networks, and infrastructures, monitoring them for optimal functionality, troubleshooting for any errors, and overseeing their security and integrity.
Why is information technology important?

Data powers industries worldwide, and it is hard to find a competitive organization that does not depend on insights from data in the world today.
Information technology has traversed virtually every industry as it provides the grounds for maximum possible business outputs in any operation it is applied.
Information technology provides organizations with a means to process and manage the electronic data of their users.
Considering the large sets of data generated in healthcare, even as a single patient can generate about 80 megabytes of data yearly, it is no wonder information technology is the crux of many healthcare operations in the world today.
Healthcare facilities, both large and small, collect and keep patient and user data, and some go on to process, analyze, and secure the data turning it into useful information.
Components of information technology
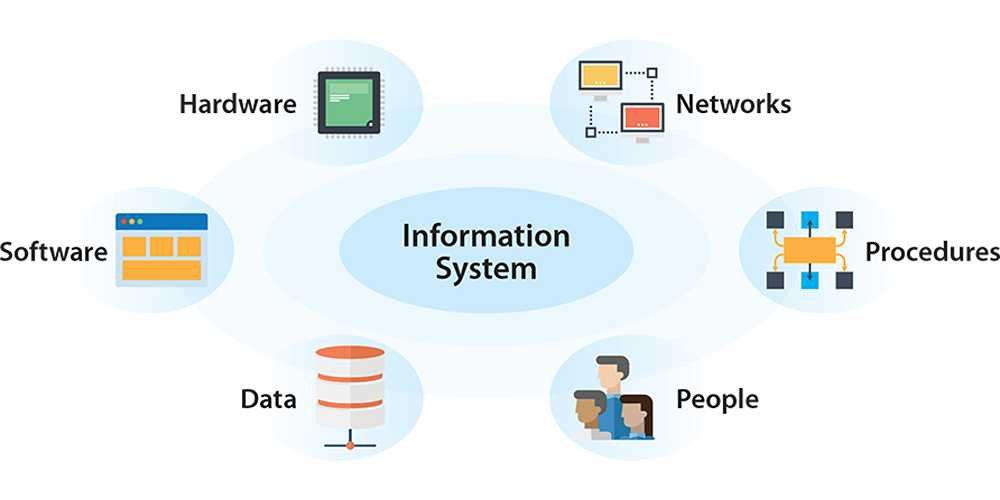
1. Hardware
These are the physical components of an information system, the computer devices, graphic devices, printers, scanners, global positioning systems (GPS), etc that work with data and can be as small as a smartphone or as large as a supercomputer that fills a building.
Computer accessories like keyboards, mice, etc are included as well.
Storage is also a type of hardware – any technology that holds information as data locally on a specific server or is shared among many remote servers.
Storage may be on-premises or accessed via a cloud service, examples include random-access memory (RAM), tape, hard disk drives, and solid-state drives.
Others include computer chips, motherboards, and memory chips that reside in the computer case and are not usually visible from the outside.
2. Software
Software is a set of instructions that tells the hardware what to do hence, it is not tangible and cannot be touched.
Software is created by computer programmers who outline and compile instructions for the hardware to run with to manipulate data, process information, and perform designed tasks.
The software can be broadly divided into two, including operating systems software that forms an interface between the hardware and users and runs other software on the hardware setup and application software that is designed for particular sets of tasks like handling a spreadsheet, creating a document, etc
Examples of operating system software include Microsoft Windows and Apple iOS while internet browsers like Google Chrome, databases like SQL, email servers like Microsoft Exchange, etc are examples of application software.
3. Data
Data is a collection of non-disputable raw facts and figures – texts, images, etc, that are largely unorganized and later processed to generate information.
This is what all other components of information technology work with.
Organizations collect all kinds of data, analyze it, and use it to make decisions toward achieving organizational operational efficiency.
Data helps organizations achieve their aim and stay competitive.
As the hardware can’t work without software the same as software needs data for processing.
Data is stored in databases and data warehouses.
Databases managed data using database management systems.
Data warehouses however are common storage options for big data where the data is stored in its raw unprocessed form from where advanced analytics operations are performed.
4. Networks
This component connects all hardware devices in an information system together to form a network.
The connections can be through wire cables e.g. Ethernet cables and fiber optics, or via wireless, such as Wi-Fi.
A network can connect computers in a specific area through a local area network (LAN) or computers in remote locations via a wide area network (WAN).
Since a computer can function standalone, network technologies have made it easy to connect with another computer thereby easing information flow among them.
The Internet can be considered the largest network there is, a network of networks.
5. People
Information technology came into being to ease communication between humans, people built computers for people to use and communicate.
The people component of information technology is the human element of the system and constitutes the people that are needed to run the system including technical developers and designers (people who design the technologies used to build the information system), support personnel (people who help end-users understand and use the system e.g. data center support, help-desk support, etc), business professionals (e.g. CEOs, managers, etc that own and/or run the information system business) and the end-users (e.g a patient, the general public).
6. Procedures
These are the guidelines and standards in information systems that organizations use to improve their operations to stay competitive and achieve their desired goals.
Information systems are being integrated with organizational processes to deliver value to businesses in several ways including revenue generation, cost-saving, etc.
Obisesan Damola
Damola is a medical doctor who has worked in the Nigerian healthcare industry for a little over 3 years in a number of primary, secondary, and tertiary hospitals. He is interested in and writes about how technology is helping to shape the healthcare industry. He graduated from the College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, the foremost medical training institution in Nigeria.



