AI solutions are transforming the way healthcare is delivered around the world, ultimately helping to reduce healthcare costs while improving patient outcomes.
AI is currently being used to create clinical decision support systems and extract useful insights from large sets of health data.
Furthermore, AI has the potential to improve hospital care, assist clinical research, discover new treatments, detect and predict disease, aid drug development, and improve healthcare insurance, among other things.
1. Radiology and medical imaging
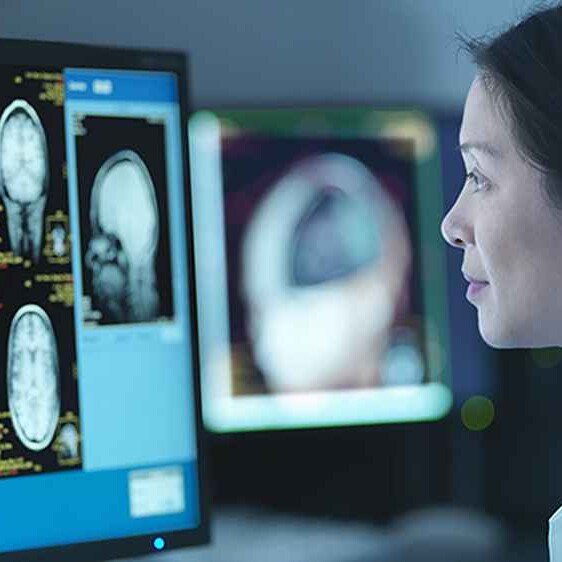
Deep learning is being applied in the field of radiology to efficiently review medical scan images and offer diagnoses with high accuracy, saving radiologists the time and effort of manually reviewing scans.
Aside from making a diagnosis from medical scans, this technology also helps identify minute deformities that radiographers might miss, avoiding errors in diagnosis and patient management.
An example is the IBM Watson Health Imaging solution, which was branded by a data company called Merative.
2. Clinical note transcription
Documentation takes a lot of physician time in the management of their patients.
AI, using natural language processing (NLP), helps physicians translate their speech into text form, freeing them the time needed to manually type in and document consultation notes and patient reviews.
This way, physicians can consult their patients and document their findings simultaneously. automate these repetitive tasks.
3. Computer-assisted coding (CAC)
This is a technology that uses natural language processing (NLP) to identify and match medical diagnoses, procedures, phrases, etc. within patient data to ICD-10 and CPT codes.
This helps in making sense of unstructured health data in text form, and this is especially useful in clinical reporting, medical claims reporting, and health data management.
NLP can accurately scan and analyze medical records and derive relevant information from large healthcare data sets in medical records buried in text format.
Therefore, it can easily and accurately interpret health data, drawing conclusions that EHRs cannot.
4. Remote care and monitoring
In telemedicine, AI technologies help physicians monitor patient health from the comfort of their homes.
This remote care involves continuous vital sign checks, sleep pattern monitoring, etc.
These AI technologies are intelligent enough to flag an abnormal finding in a patient’s clinical status and notify concerned bodies, including the patient or their caregivers, physicians, etc., to take the appropriate steps immediately to combat the abnormality.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices also similarly utilize AI to manage user health data and optimize recommendations for maintaining their good health.
This includes smartphone applications and fitness devices like Fitbits, Apple watches, etc.
5. First-time right diagnosis
Getting a patient diagnosis right at the first visit is essential to offering the best management plan for the patient, improving health outcomes, and optimizing healthcare resources.
A missed diagnosis stresses patients out, wasting their time and finances, and delaying appropriate treatment.
It also demands added effort and time from physicians for a repeat review and contributes to the wastage of healthcare resources.
AI deep learning algorithms assist physicians in making the appropriate diagnoses in pattern-centric fields like radiology and pathology; they are faster, can identify minute abnormalities, and offer accurate recommendations about scan images towards making the right diagnosis.
6. Virtual health assistants and chatbots
These are AI platforms developed to offer some virtual medical assistance to users, as a human health professional would.
These healthcare solutions can be web-based and/or mobile applications and can offer personalized services including symptom checks, virtual diagnostic tools, health risk assessment, health recommendations, navigation systems, and monitoring of chronic medical conditions.
Some of these AI platforms are so intelligent that users do not realize they are not interacting with a human, and of course, they offer options to initiate contact with a human health professional should the user desire.
Users interact with the platform, answer questions related to their health, and thereafter receive recommendations concerning their responses.
An example is Sensely’s chatbot, Molly.
7. Disease prediction
Machine learning is well known for its predictive feature that reviews health data to access correlations and trends toward predicting the occurrence and course of diseases.
This way, health professionals can utilize data to ‘see’ into the future, forecast possible health outcomes, and take adequate steps to combat or reduce the onset of any diseases that might occur before they occur.
This is especially useful in screening for chronic conditions like diabetes, cancer, etc.
8. Health data management
Health data is big data! Patient data is generated in large volumes daily.
Artificial intelligence is being applied in the management of these large health data sets, including the analysis of health data and the use of machine learning models in data science to derive insights from data, automate data processes, and make future predictions.
This helps accelerate clinical decision-making in healthcare, improving the efficiency of the health industry and the quality of care.
9. Equitable healthcare
Artificial intelligence is impartial and devoid of human emotions.
Government and health organizations have a responsibility to create healthcare systems that offer equitable and unbiased healthcare to their users without consideration of race, gender, or socioeconomic factors.
AI technologies help eliminate these intricate human biases that are hard to detect or eliminate and establish an equitable approach to healthcare delivery, leading to optimal health outcomes for everyone.
This way, personalized care is achievable in that clinical decisions would be made objectively since machine learning algorithms offer unbiased, data-driven recommendations.
10. Automated administrative tasks
Using machine learning models, AI is helping with routine, repetitive administrative tasks to minimize human errors and maximize efficiency.
These machines complete the time-consuming tasks that humans once did and therefore allow healthcare professionals to focus on more patient-centred tasks.
Ultimately, these AI systems help save on the costs of running health facilities.
Obisesan Damola
Damola is a medical doctor who has worked in the Nigerian healthcare industry for a little over 3 years in a number of primary, secondary, and tertiary hospitals. He is interested in and writes about how technology is helping to shape the healthcare industry. He graduated from the College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, the foremost medical training institution in Nigeria.