Jump to...
Artificial intelligence in healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) solutions are transforming the way healthcare is delivered around the world, ultimately helping to cut down healthcare costs while improving patient outcomes.
Currently, AI has been used to develop clinical decision support systems and gain useful insights from large sets of health data.
Also, AI has the potential to improve hospital care, aid clinical research, discover new treatments, detect and predict disease, aid drug development, improve healthcare insurance, etc.
Healthcare AI market statistics
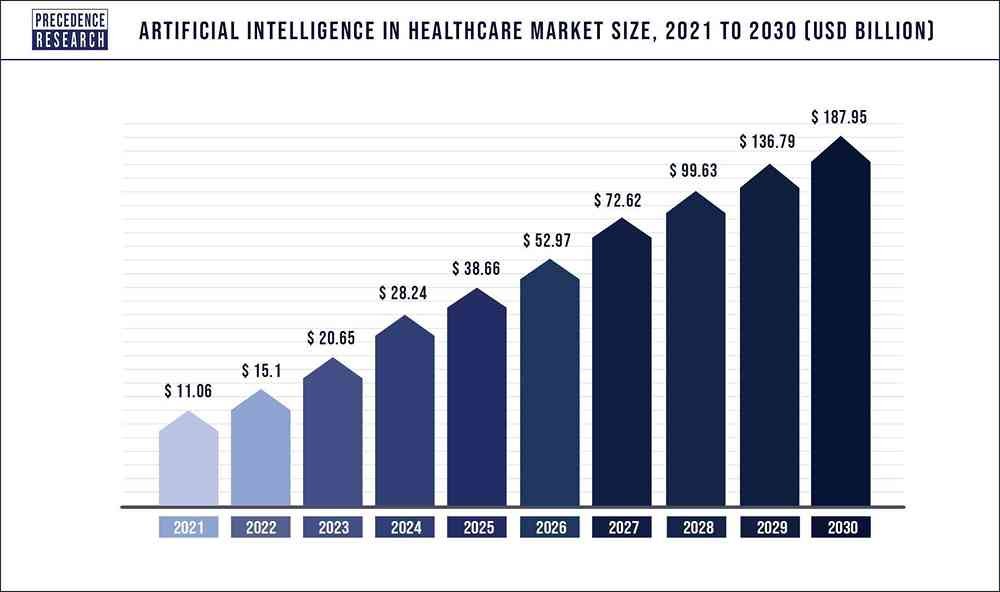
According to a report by Precedence Research, global artificial intelligence in the healthcare market was estimated at US$ 11.06 billion in 2021 and is expected to surpass around US$ 187.95 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 37% during the forecast period of 2022 to 2030.
The global investment in healthcare AI rose to a record-breaking $2.5 billion during the first quarter of 2021 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 48% between 2017 and 2023. – Business Insider.
It then does not come as a shock that the number of startups developing AI solutions in healthcare is growing at an unprecedented speed.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology concerned with replicating human intelligence in computer systems and building smart machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence.
These machines can mimic cognitive functions of the human mind, such as “learning” and “problem-solving.”
The purpose of AI is to aid human capabilities in observing activities and helping us make advanced decisions.
It is especially useful in automating tedious repetitive processes without any fatigue and analyzing data much faster and more accurately than humans.
While AI has numerous potential applications in several industries, organizations commonly use AI to improve the efficiency of their work processes, derive insight from their data, automate decision-making and resource-heavy tasks, make future predictions based on data, and gain an advantage over their competitors.
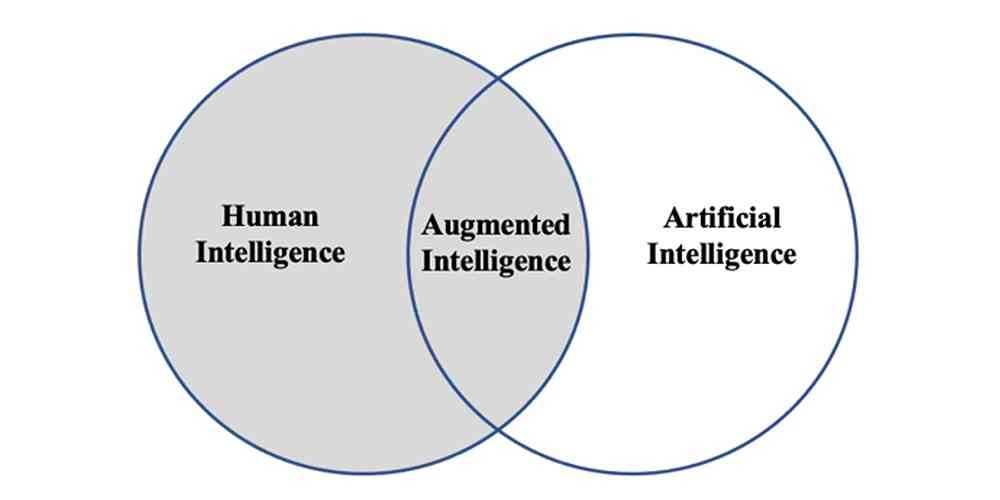
The term artificial intelligence is commonly linked to a superintelligent AI whose intelligence transcends human intelligence, which would be created in the future—the singularity (technological).
This type of AI is called artificial general intelligence (AGI), which is yet to be created.
The current “weak” AI systems mainly serve assistive roles for humans in industries around the world.
To distinguish between AGI and weak AI, the term Augmented intelligence was coined to refer to AI systems in assistive roles.
Worthy of note, some refer to augmented intelligence as cognitive computing.
How AI works

Artificial intelligence is the most complex creation of humanity yet, and it has been touted as our final invention—a technology that would invent advanced tools and services unsupervised that would exponentially change how we lead our lives.
To replicate human intelligence, AI requires hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms, an ability that helps it learn, reason, or make decisions and correct itself.
Human intelligence, in learning and making decisions, is based on information about a subject of concern and experience about the subject.
For AI machines, information and experience are provided using large amounts of labeled training data.
AI processes this data, analyzes it for correlations and patterns, and uses the patterns to make predictions.
Hence, AI works using three cognitive processes:
- learning (acquiring data and creating algorithms for turning the data into actionable information),
- reasoning (identifying and choosing the right algorithm to arrive at the desired outcome), and
- self-correction (fine-tuning AI algorithms to continually provide the most accurate results)
Types of AI (based on capability)
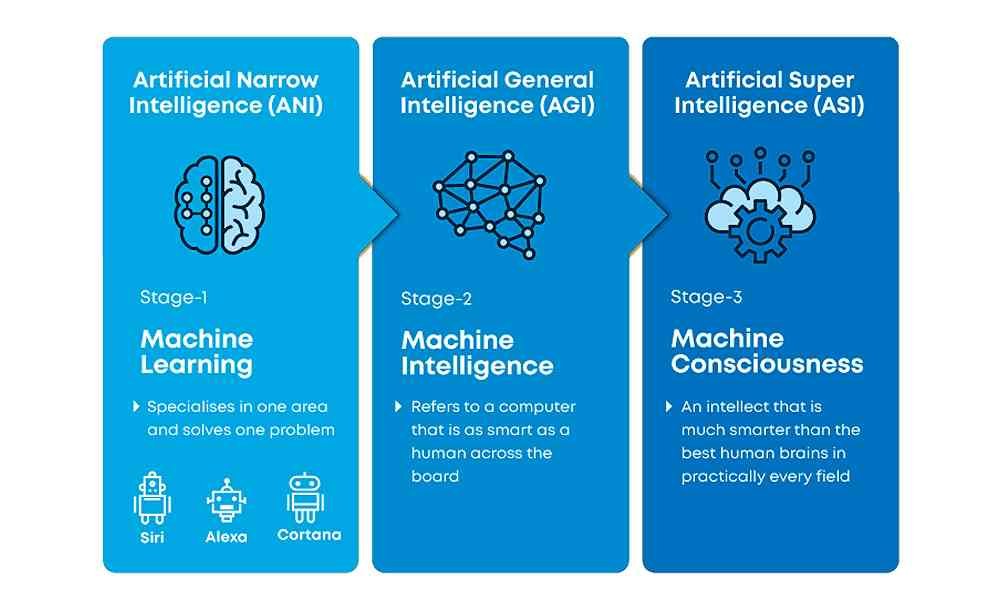
1. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
Narrow AI is the most successful realization of artificial intelligence in the world today; it represents all the existing AI, including even the most complicated and capable AI that has ever been created.
Sometimes referred to as “weak AI,” narrow AI operates within a limited context, designed to focus on performing a single or specific task extremely well.
It has experienced breakthroughs in the last decade that have had “significant societal benefits; Google search engines, self-driving cars, Apple’s Siri, and Amazon’s Alexa are common examples.
While these machines may seem intelligent, they are operating under far more constraints and limitations than even the most basic human intelligence, as they can do nothing more than what they are programmed to do.
2. Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
This is the ability of an AI to learn, perceive, understand, and function exactly like a human being.
Sometimes referred to as “Strong AI,” AGI has long been the go-to for science fiction movie makers, in which super-intelligent robots overrun humanity.
Examples include the machines from the sci-fi movie Westworld.
AGI is a machine with general intelligence that it can apply to solve any problem, much like a human being.
The creation of a machine with human-level intelligence is the Holy Grail for many AI researchers, but time hasn’t eased the difficulty of essentially creating a machine with a full set of cognitive abilities.
This will make AI systems just as capable as humans by replicating our multi-functional capabilities.
3. Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
An ASI machine would be able to surpass all human capabilities, and the development will mark the pinnacle of AI research as ASI will become the most capable form of intelligence on earth.
In addition to replicating the intelligence of human beings, it will be exceedingly better at everything it does because of its greater memory, faster data processing, and analysis.
It will make better decisions, make rational decisions, build emotional relationships, etc
This will stem from the point at which we build AGI, as AI systems will rapidly be able to improve their capabilities and advance into realms that we might not have dreamed of.
The development of AGI and ASI will lead to a scenario most commonly referred to as a singularity.
There is a long way to go before we get there, as the current state of AI development is still rudimentary.
Types of AI (based on functionality)
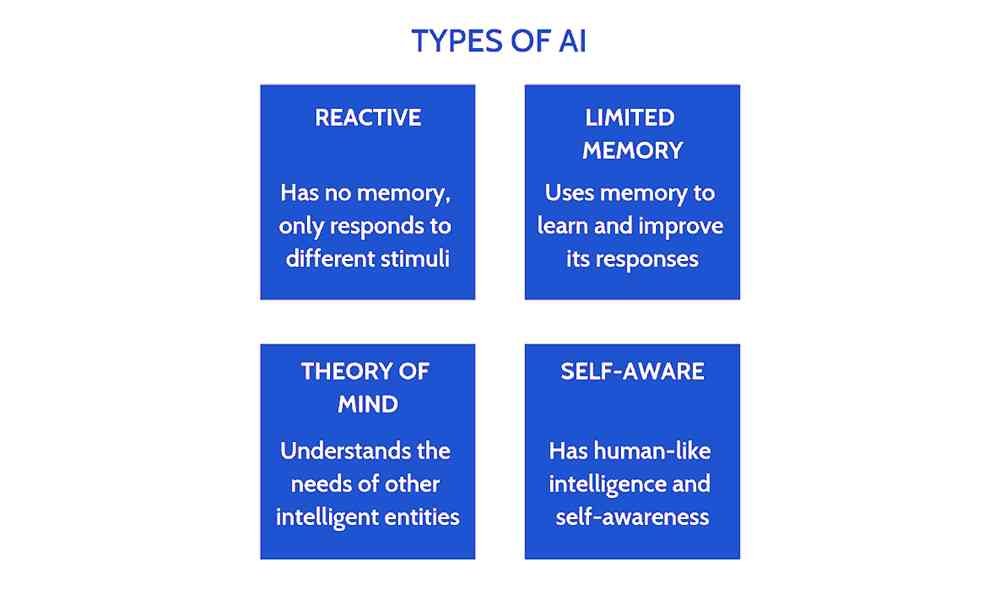
1. Reactive Machines
These are the oldest forms of AI, with extremely limited capacity.
A reactive machine follows the most basic of AI principles; it is capable of only using its intelligence to perceive and react to the world.
It emulates the human mind’s ability to respond to different kinds of stimuli.
These machines do not have memory-based functionality.
This means these machines cannot rely on past experiences to inform decision-making, i.e., they cannot “learn.”
Though limited in scope, reactive machine AI can attain a level of complexity and offer reliability when created to fulfill repeatable tasks.
This type of AI is more trustworthy and reliable; it will react the same way to the same stimuli every time.
Examples include IBM’s Deep Blue, Google’s AlphaGo, etc.
These AI systems have no memory and are task-specific.
2. Limited Memory
These AIs can learn from the history and data of previous events to make decisions.
They can store previous data and make predictions from the stored data.
They essentially look into the past for clues on what may come next.
Almost all present-day AI applications, from virtual assistants to self-driving cars, are driven by limited-memory AI.
This includes those that make use of deep learning and are trained by large volumes of data designed for machine training, stored in their memory to form a reference for solving future problems.
For example, an image recognition AI is trained using thousands of images with labels to teach it to name objects it scans.
When an image is scanned, it uses the training images as references to understand the contents of the image presented to it, and based on its “learning experience,” it labels new images with increasing accuracy.
3. Theory of Mind
The world has not yet achieved the technological and scientific capabilities to reach this level of artificial intelligence.
Theory of mind AI is the next level of AI that researchers are currently engaged in developing.
The concept is based on the psychological premise of understanding that living things have thoughts and emotions that affect their behavior.
This AI will be able to understand the entities it is interacting with by discerning their needs, emotions, beliefs, and thought processes—social intelligence.
This would mean that AI could understand how humans, animals, and other machines feel and make decisions, and then utilize that information to make decisions of their own.
This is because to truly understand human needs, AI machines will have to perceive humans as individuals whose minds can be shaped by multiple factors.
4. Self-awareness
Also currently theoretical, self-awareness is the final stage of AI development after establishing the theory of mind.
This is the ultimate objective of all AI research.
Self-awareness in AI relies on human researchers understanding “human consciousness” and then learning how to replicate it so that it can be built into machines.
This type of AI possesses human-level consciousness and understands its existence in the world, as well as the presence and emotional state of others.
It will not only understand and evoke emotions in those it interacts with, but it will also have emotions, needs, and potential desires of its own.
This is the type of AI that doomsayers of the technology are wary of!
Components of AI
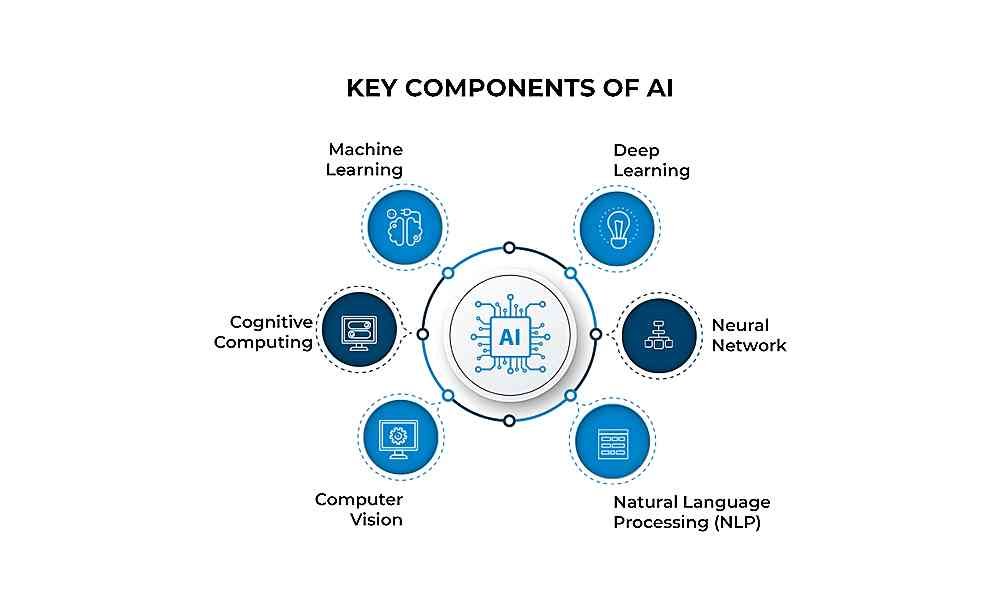
There are several AI technologies, including machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), etc.
As depicted by the image, DL is a subset of ML, which is also another subset of AI.
AI is an umbrella discipline that covers everything related to making machines smarter.
ML, DL neural networks, etc. are subsets of AI.
While machine learning and deep learning will be discussed further in this post, other technologies in AI include the following:
- Neural networks: a set of algorithms modeled after the human brain that endeavor to identify underlying relationships in a set of data. They are also known as artificial neural networks (ANNs) or neural nets.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): a machine’s ability to decipher and understand human language as it is spoken and written. and offer a response or result.
- Computer Vision: This refers to technologies that enable computers to ‘see’ and understand digital images and videos, draw meaningful inferences from them, and thereafter take actions or make recommendations based on the inferences.
Obisesan Damola
Damola is a medical doctor who has worked in the Nigerian healthcare industry for a little over 3 years in a number of primary, secondary, and tertiary hospitals. He is interested in and writes about how technology is helping to shape the healthcare industry. He graduated from the College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, the foremost medical training institution in Nigeria.