Data management
In today’s digital economy, companies have access to more data than ever before.
Data is seen as a corporate asset that can be used to make more informed business decisions.
The amount, variety, and speed of big data make it so valuable to organizations in terms of improving and accelerating product development, customer experience, security, operational efficiency, etc.
Given the important role of big data in running successful businesses, strong management practices and a robust management system are essential for every organization to take advantage of insights from data.
Big data management is the organization, administration, and governance of large volumes of both structured and unstructured data, the goal of which is to ensure a high level of data quality needed for business intelligence and big data analytics applications.
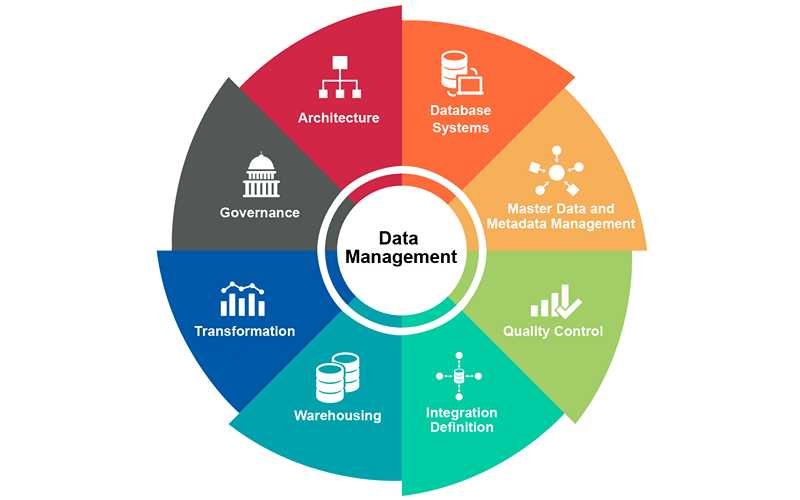
The data management process includes a combination of different functions that collectively aim to make sure that the data in corporate systems is accurate, available, and accessible.
The best data management software ensures that reliable, up-to-date data is always used to drive decisions, from data preparation to cataloging, searching, and governance, allowing people to quickly find the information they need for analysis.
A lack of proper data management can saddle organizations with incompatible data silos, inconsistent data sets, and data quality problems that limit their ability to run business intelligence (BI) and analytics applications.
This data creates a foundation of intelligence for important business decisions.
The importance of data management
- Insight for organizations to make better decisions,
- Compliance with data privacy standards is aided by proper data management.
- Good management gives organizations a competitive advantage
- It helps minimize errors in data, hence making data more reliable for making decisions.
- Tools like authentication and encryption help to protect organizations from data losses, breaches, etc.
Challenges with managing big data
- Cultural shift: organizations often have a hard time with decision-making switching from personal insights to decisions being data-driven.
- Data silos: inconsistent data stored in different databases.
- Data complexity: these data are largely unstructured and hence exist in different forms.
- Data quality: the disorder of unstructured data as well as human error, e.g., typography, introduces poor quality.
- Data storage: these data often require cloud storage, and their transfer between platforms can be very slow.
- Lack of data professionals: dealing with big data requires data experts, roles largely in demand.
Data management roles
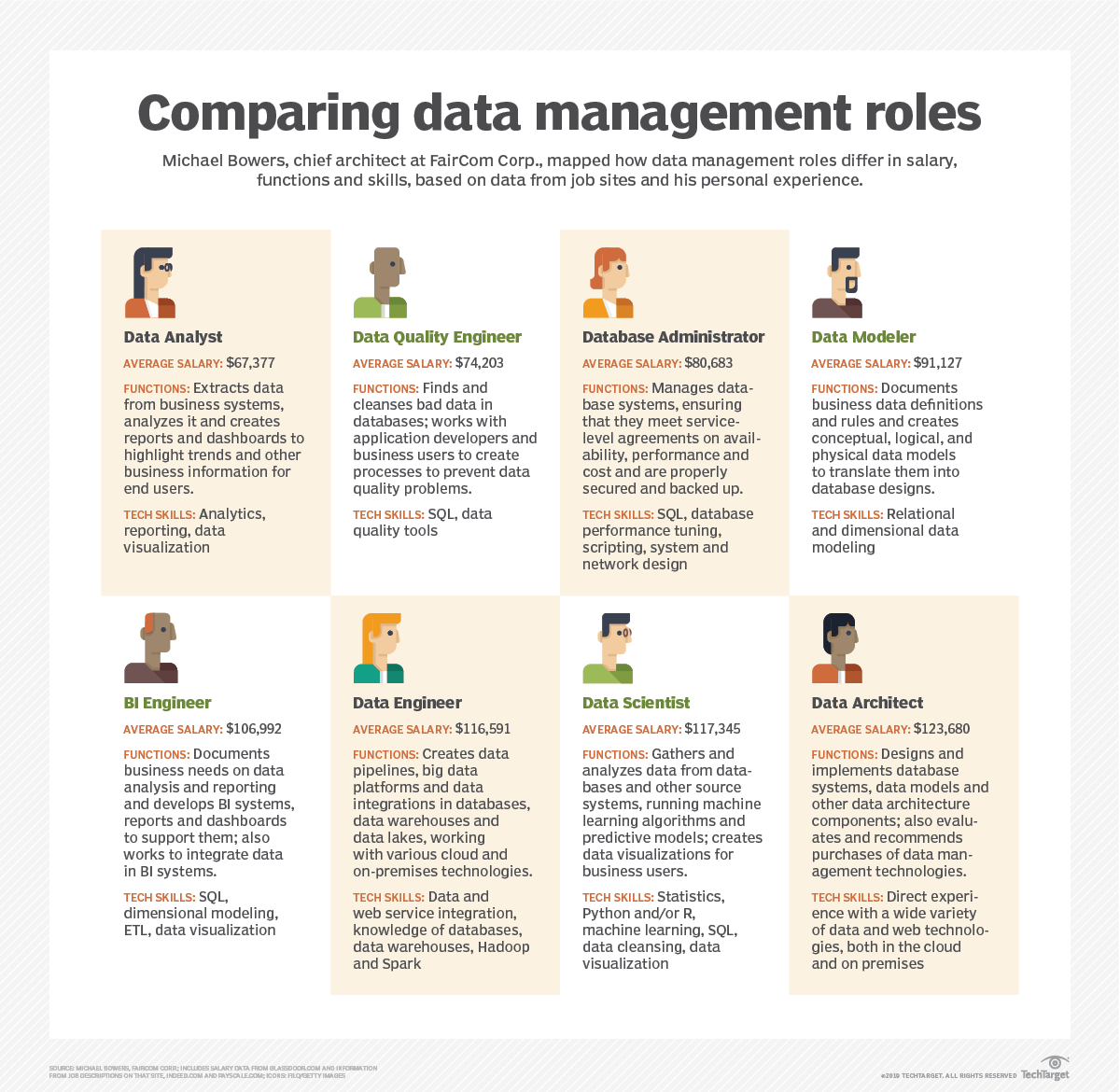
In smaller organizations with limited resources, individual workers may handle multiple roles.
Data management roles can also easily overlap in skills.
But in general, data management professionals include
- Data scientist
- Data analyst
- Data Engineer
- Business intelligence engineer
- Database administrators (DBAs)
- Database developers
- Data quality analysts and engineers
- Data integration developers
Obisesan Damola
Damola is a medical doctor who has worked in the Nigerian healthcare industry for a little over 3 years in a number of primary, secondary, and tertiary hospitals. He is interested in and writes about how technology is helping to shape the healthcare industry. He graduated from the College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, the foremost medical training institution in Nigeria.