DNA paternity testing, also known as paternity testing or DNA paternity testing, is a scientific method used to determine biological parentage between a child and an alleged father.
This type of DNA test has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its accuracy, reliability, and ease of use.
In this blog post, we will explore the ins and outs of the DNA paternity test, including how it works, its uses, benefits, limitations, and considerations.
What is the DNA paternity test?
DNA paternity testing, also known as parentage testing, is a process of comparing DNA profiles to establish biological relationships between individuals.
It relies on the fact that half of an individual’s DNA is inherited from their biological mother and the other half from their biological father.
By analyzing specific genetic markers, scientists can determine whether an alleged father is biologically related to a child with a high degree of certainty.
One of the main benefits of the test is its accuracy and reliability.
It can provide conclusive evidence of biological parentage with an accuracy rate of over 99.9%.
Additionally, it is non-invasive and requires only a simple cheek swab or blood sample from the child and alleged father, making it safe and painless.
Furthermore, it can be conducted quickly, with results typically available within a few days to a week.
How does the test work?
Paternity DNA testing relies on the comparison of genetic markers, known as DNA sequences, between the child and the alleged father.
The most common method used for paternity testing is called short tandem repeat (STR) analysis, which examines specific regions of the DNA where variations in the number of repeated sequences occur.
By comparing the patterns of DNA repeats between the child and the alleged father, scientists can determine the likelihood of biological relatedness with a high degree of accuracy.
The significance of the test

DNA paternity testing holds significant importance in various situations, including:
- Legal proceedings: Paternity testing is often required in legal cases involving child support, custody disputes, inheritance claims, and immigration applications. Court-admissible DNA testing can provide irrefutable evidence of biological relationships, influencing legal decisions and outcomes.
- Personal peace of mind: Individuals may choose to undergo paternity testing for personal reasons, such as resolving doubts or suspicions about biological parentage. Knowing the truth can offer peace of mind and closure, fostering healthier family dynamics and relationships.
- Medical history and genetic counseling: Accurate knowledge of biological parentage is essential for obtaining accurate medical histories and genetic information. This information can be crucial for assessing the risk of inherited genetic conditions and guiding medical management and genetic counseling.
Types of the DNA paternity test
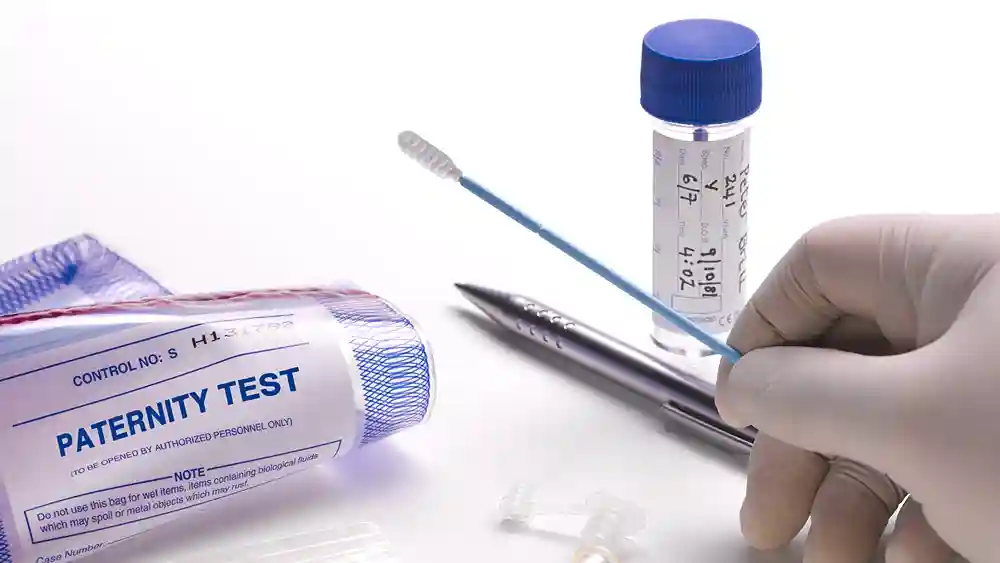
1. Standard DNA paternity test
The standard DNA paternity test, also known as the trio test, involves comparing DNA samples from the alleged father, child, and, if available, the biological mother.
This test analyzes specific genetic markers, known as short tandem repeats (STRs), to determine paternity.
- Accuracy: Standard DNA paternity tests are highly accurate, with results typically showing a probability of paternity exceeding 99.9% when the alleged father is indeed the biological father.
- Suitability: The standard DNA paternity test is suitable for most paternity cases, providing robust results with a high degree of certainty.
2. Non-invasive prenatal paternity test
Non-invasive prenatal paternity testing allows individuals to establish paternity before the child is born, using maternal blood samples.
This test analyzes cell-free fetal DNA present in the mother’s bloodstream, comparing it to the alleged father’s DNA.
- Accuracy: Non-invasive prenatal paternity testing is highly accurate, with results comparable to those of standard DNA paternity tests. However, it may have a slightly higher chance of inconclusive results due to the lower concentration of fetal DNA in maternal blood.
- Suitability: This type of test is suitable for individuals who wish to establish paternity during pregnancy without invasive procedures such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
3. Home DNA paternity test
Home DNA paternity tests are self-administered kits that allow individuals to collect DNA samples at home using buccal (cheek) swabs.
The samples are then sent to a laboratory for analysis, and results are typically provided via mail or online.
- Accuracy: Home DNA paternity tests conducted by reputable laboratories are generally accurate. However, it’s essential to choose a reliable testing provider and follow the instructions carefully to ensure accurate results.
- Suitability: Home DNA paternity tests are suitable for individuals seeking convenience and privacy. They may be used for personal peace of mind but may not be admissible as evidence in legal proceedings without proper chain-of-custody documentation.
4. Legal DNA paternity test
Legal DNA paternity tests are conducted following strict chain-of-custody procedures to ensure the admissibility of results in legal proceedings.
Samples are collected by a trained professional, and participants must provide photo identification and sign consent forms.
- Accuracy: Legal DNA paternity tests are held to stringent standards to ensure accuracy and reliability. Results obtained through legal testing are considered legally binding and admissible in court.
- Suitability: Legal DNA paternity tests are suitable for cases involving child support, custody disputes, inheritance claims, or immigration applications where court-admissible evidence is required.
How is the test done?
1. Selecting a testing provider
Before proceeding with DNA paternity testing, it’s essential to choose a reputable testing provider.
Look for accredited laboratories with a track record of accuracy and reliability.
Consider factors such as turnaround time, cost, and accreditation by organizations.
2. Ordering the test Kit
Once you’ve selected a testing provider, order a DNA paternity test kit from their website or contact their customer service.
The kit typically includes buccal (cheek) swabs for sample collection, consent forms, and detailed instructions for collecting and returning samples.
3. Sample collection
Follow the instructions provided in the test kit for sample collection.
The process typically involves the following steps:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling the swabs to prevent contamination.
- Open the packaging for the buccal swabs and remove them from the sterile packaging.
- Gently swab the inside of your cheek for about 30–60 seconds using the provided swabs. Repeat this process for each individual participating in the test, including the alleged father, child, and biological mother (if available).
- Allow the swabs to air dry for a few minutes before placing them back into the provided envelopes or containers.
4. Completing consent forms
Fill out any necessary consent forms included in the test kit.
These forms may require basic information such as names, dates of birth, and signatures of all parties involved in the testing.
Ensure that all information is accurate and complete to avoid delays in processing.
5. Packaging and returning samples
Once the samples are collected and consent forms are completed, package them according to the instructions provided in the test kit.
Typically, this involves placing the swabs and consent forms in the provided envelopes or containers and sealing them securely.
- Double-check that all samples and documents are properly labeled to ensure accurate identification.
- Follow the shipping instructions provided by the testing provider to return the samples to the laboratory. This may involve using prepaid shipping labels or arranging for courier services.
6. Laboratory analysis
Upon receiving the samples, the laboratory begins the process of DNA analysis.
Highly trained technicians extract DNA from the buccal swabs and analyze specific genetic markers, known as short tandem repeats (STRs) or microsatellites.
7. Comparison and interpretation
The DNA profiles of the alleged father and child are compared to assess genetic similarities.
A paternity index is calculated based on the observed genetic markers, indicating the likelihood of paternity.
A high paternity index suggests a high probability of paternity, while a low index indicates exclusion of paternity.
8. Receiving results
Once the analysis is complete, the testing provider sends the results to the participants.
Results are typically provided in a formal report format, detailing the probability of paternity based on the DNA analysis.
Considerations before the test
Before undergoing DNA paternity testing, individuals should consider the following:
- Consent: All parties involved in the testing, including the alleged father, child, and biological mother (if available), must provide informed consent for the procedure.
- Accuracy and Reliability: DNA paternity testing is highly accurate when performed by accredited laboratories using appropriate protocols. However, it’s essential to choose a reputable testing provider to ensure reliable results.
- Emotional Impact: The results of paternity testing can have profound emotional consequences for individuals and families. It’s crucial to prepare for potential outcomes and seek appropriate emotional support if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is DNA paternity testing?
DNA paternity testing is a scientific method used to determine biological relationships between individuals, specifically to establish the biological father of a child.
It compares DNA profiles to assess genetic similarities and determine paternity with a high degree of accuracy.
2. How does DNA paternity testing work?
DNA paternity testing involves collecting DNA samples from the alleged father, child, and, if available, the biological mother.
Samples are typically collected using buccal (cheek) swabs and sent to a certified laboratory for analysis.
Highly trained technicians extract DNA from the samples and analyze specific genetic markers to determine paternity.
3. Is DNA paternity testing accurate?
Yes, DNA paternity testing is highly accurate when performed by accredited laboratories using appropriate protocols.
The accuracy of the test depends on factors such as the quality of the samples, the number of genetic markers analyzed, and the expertise of the testing provider.
4. How long does DNA paternity testing take?
The turnaround time for DNA paternity testing varies depending on the testing provider and the type of test requested.
In most cases, results are available within 3 to 5 business days after the laboratory receives the samples.
5. Do both parents need to participate in DNA paternity testing?
Ideally, DNA samples should be collected from both the alleged father and the child to establish paternity with the highest level of accuracy.
If the biological mother is available, her participation can further enhance the accuracy of the test and provide additional information.
6. Is DNA paternity testing invasive or painful?
No, DNA paternity testing is non-invasive and painless.
Samples are collected using buccal swabs, which involve gently swabbing the inside of the cheek to collect cells for DNA analysis.
There are no needles or blood draws involved in the process.
7. Can DNA paternity testing be performed before the child is born?
Yes, prenatal paternity testing is available for individuals who wish to establish paternity before the child is born.
This typically involves procedures such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), which carry certain risks and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
8. Is DNA paternity testing admissible in court?
Yes, DNA paternity testing conducted by accredited laboratories using appropriate protocols is admissible as evidence in legal proceedings.
Court-admissible DNA testing follows strict chain-of-custody procedures to ensure the integrity of the samples and results.
9. Can DNA paternity testing determine other biological relationships?
Yes, DNA paternity testing can be used to establish other biological relationships, such as maternity, sibling relationships, or grandparentage.
The same principles of DNA analysis used in paternity testing apply to these other relationships.
10. How do I choose a reputable DNA paternity testing provider?
When selecting a DNA paternity testing provider, look for accredited laboratories with a proven track record of accuracy and reliability.
Consider factors such as accreditation by organizations like AABB or ISO, turnaround time, cost, and customer reviews.
Limitations of the test
While paternity DNA testing is highly accurate and reliable, it is not without limitations.
In cases where the alleged father is unavailable or unwilling to participate in testing, alternative methods such as kinship testing or genetic reconstruction may be used to infer paternity.
Additionally, it is essential to choose a reputable and accredited DNA testing laboratory to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the emotional and psychological implications of paternity DNA testing, as the results can have profound effects on individuals and families.
Obisesan Damola
Damola is a medical doctor who has worked in the Nigerian healthcare industry for a little over 3 years in a number of primary, secondary, and tertiary hospitals. He is interested in and writes about how technology is helping to shape the healthcare industry. He graduated from the College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, the foremost medical training institution in Nigeria.